What Is Developing Trend of CTP Plate
Laser Computer-to-Plate (CTP) technology is a modern pre-printing process technology. Specifically, CTP technology refers to using a computer to record digitized page information (including text, images, etc.) directly onto the printing plate through laser exposure, thereby generating a printing plate that can be directly used for printing.
In recent years, with the rapid development of laser technology and computer technology, the CTP market has also shown rapid growth. The progress of laser computer direct plate making technology is mainly reflected in the improvement of equipment performance, acceleration of plate making speed and improvement of printing plate quality.

With the continuous innovation of core technologies such as laser light sources and control systems, the stability, accuracy and reliability of CTP equipment have been significantly improved. North America, Europe, Asia and other regions are the main markets in the global laser computer-to-plate market.
Among them, North America has a large demand for CTP technology due to the maturity of the printing industry; CTP technology has been widely used in Europe due to its emphasis on environmental protection and high-quality printing; in Asia, especially China, with the rapid development of the printing industry and the increase in market demand, the China plate printing market has also shown a rapid growth trend.
Laser computer direct platemaking technology is widely used in packaging printing, commercial printing, publishing printing and other fields. With the continuous advancement of laser technology, CTP technology has gradually been applied in flexographic printing, screen printing and other fields. In the future, the challenges faced by the laser computer direct platemaking market include technological upgrading, intensified market competition, and environmental protection regulations.
But at the same time, with the rise of digital printing and green printing, CTP technology is also facing new development opportunities. The printing industry's demand for high-quality, high-efficiency, and low-cost platemaking technology will continue to drive the growth of the CTP market.
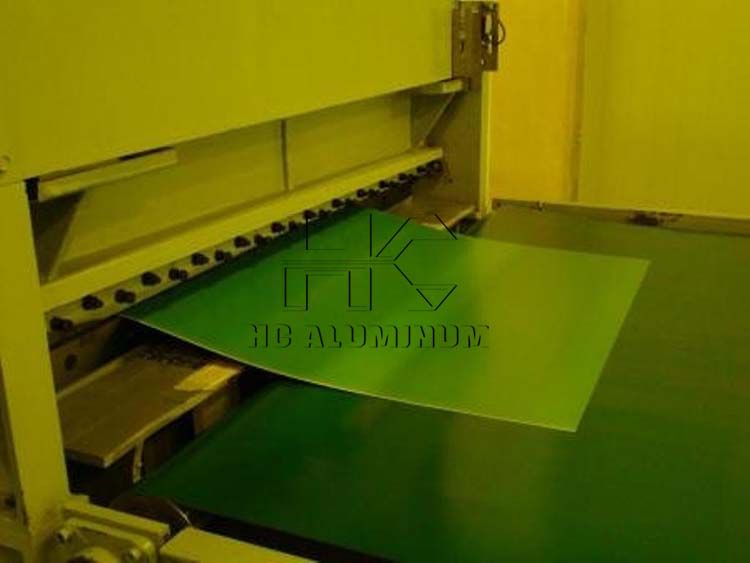
From the perspective of technology, as the global offset printing plate production and manufacturing pattern shifts to China, our country has become a major offset printing plate production country. Most ctp plate manufacturers including HC printing have built continuous roll-to-roll production lines, realizing large-scale production of offset printing plates, and the overall production technology level of the industry is relatively mature.