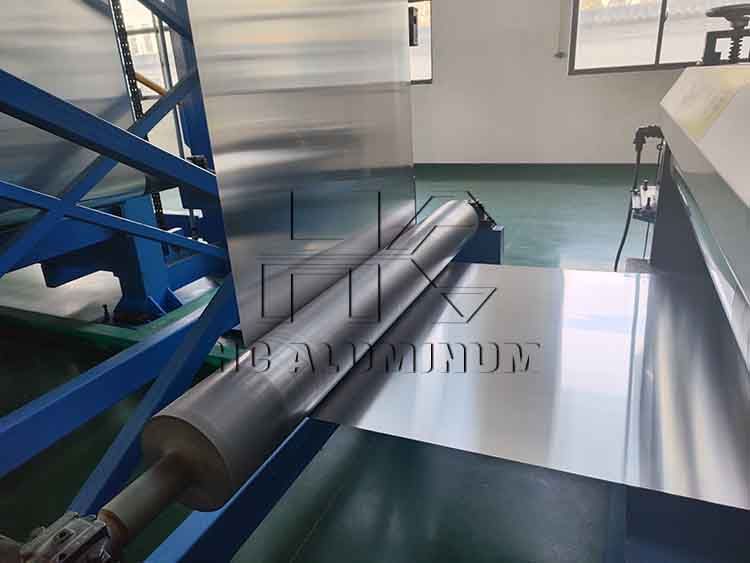
How to Develop PS and CTP Plate
After exposure, the PS plate must be developed to form an image to become a printing plate for printing on the machine. The development of the PS plate is actually to dissolve the resin decomposed by exposure with an alkaline solvent. The process seems simple, but in order to really show a qualified printing plate, there are still strict requirements for the developer and the development process.

1. Composition of developer
The PS plate developer is mainly composed of salts formed by alkali or strong alkali and weak acid, specifically NaOH (KOH) or Na2SiO3 or a mixture of NaOH (KOH) and Na2SiO3. The developer must contain not only the main agent NaOH, KOH, or Na2SiO3 or NaOH and Na2SiO3 in a certain proportion; it must also contain a buffer, and Na2SiO3 actually has a certain buffering effect.
It should also have inhibitors, KCl or NaCl or trisodium phosphate, which are used to prevent the main developer from being neutralized by CO2 in the air in water to form acid and NaOH to reduce the drug effect during use and storage.
A certain amount of wetting agent should also be added, such as sodium dodecyl sulfonate, Tween and other surfactants. The amount should not be too much, otherwise it will easily produce a large number of bubbles and affect the development process.
2. Selection of developer
For the development of PS plates, the selection of developer is a prerequisite. As the resin used in PS plates is constantly improving, the photosensitivity of PS plates is also constantly improving. The exposure time is short, and the development often does not require too strong a developer, which not only reduces the development processing cost but also is environmentally friendly. Therefore, the traditional developer based on NaOH has evolved into a developer based on Na2SiO3, and NaOH has become a developer accelerator.
As a PS Plate manufacturer, we also have PS developer for free or sale. If users use the developer according to the dilution concentration and recommended developer processing conditions specified by the printing plate manufacturer, there will generally be no problems.
The plate-making process of traditional water-based offset CTP plates is: exposure, development, washing, protective glue application, and drying. The plate-making process of waterless offset printing CTP is: exposure, film removal, plate development, and drying.
Due to the special requirements of waterless offset printing, special waterless offset printing ink must be used during printing, and the printing press must be adjusted accordingly during the printing process. If the printing plate surface is found to be scratched or dirty during the printing process, it is necessary to use a special plate repair fluid for waterless offset CTP plates to repair the plate.